Patents
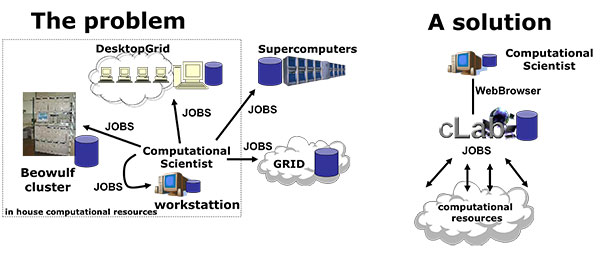
cLab: a web portal to access, use and manage computational resources
The Computational Laboratory Web Manager (cLab) is a web portal that permits the access and the management of a computational laboratory, which is a high performance hypercomputation center based on heterogeneous clusters of computers and used by multiple users simultaneously for the execution of computational jobs. cLab is an internet based application that allows users to manipulate files and folders, prepare computational tasks, submit and control them while they are running, as well as visualize or store results. cLab therefore provide tools for the users as well as for the system administrator.
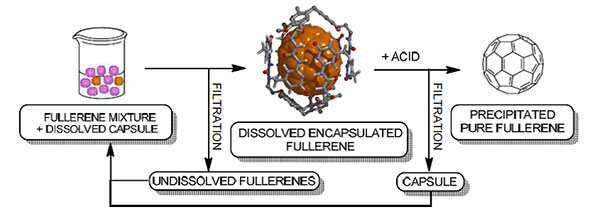
Purification of fullerenes by selective encapsulation mediated solid‐liquid extraction.
A concave compound self assembles thanks to reversible and controllable hydrogen bonding to form a dynamic capsule able to selectively extract fullerene derivatives of given size and shape. The process for the separation of fullerene derivatives is based on a sequential selective encapsulation in an appropriate solvent system of the fullerenes contained in a mixture. The capsule is formed by reversible self‐assembly of two concave fragments. The encapsulation of the fullerene derivative having the best fitting geometry for the cavity of the capsule is fast and selective.
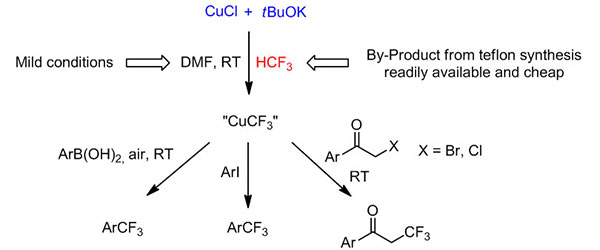
Process to obtain a trifluoromethylating composition
A process for the direct cupration of fluoroform has been developed. This exceedingly simple process employs only cheap reagents and is advantageously run at room temperature to produce CuCF3 reagents that are useful in trifluoromethylation reactions. Chemical compounds bearing a trifluoromethyl group are widely used in the production of various pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals as well as specialty materials, polymers, composites, building blocks, and intermediates for various needs. Fluoroform, CF3H, is an ideal source of CF3 because it is inexpensive, readily available in large industrial quantities, non‐toxic, and not an ozone depleter.
The technology is currently the object of a R&D collaboration between ICIQ and a global company of the crop protection sector, with the aim of finding new synthetic applications of industrial relevance for the developed trifluoromethylating agent.
Process for water oxidation comprising the use of a polyoxometalate compound as water oxidation catalyst
Conversion of sunlight energy into storable chemical energy is the major pillar of a hydrogen economy based on non-fossil fuels. Hydrogen photoproduction must be coupled with the oxidation of water to oxygen. The invention relates to the use of a cobalt-based polyoxometalate compound as a robust inorganic catalyst for the generation of oxygen from water. The catalyst allows for high turnover numbers, fast catalytic cycles and is self-repairing, which means that it does not show signs of fatigue or degradation upon time.
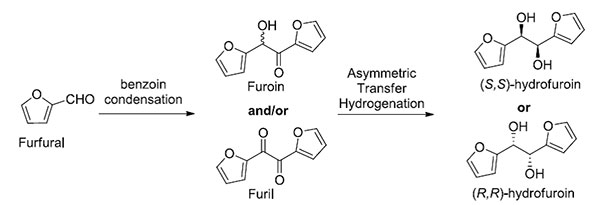
Process for the preparation of optically active 1,2-di(furan-2-yl)ethane-1,2-diol and derivatives thereof.
Conversion of biomass into high value materials is one of the challenges the chemical industry is facing. This technology, based on a two-step synthesis (benzoin condensation followed by asymmetric transfer hydrogenation) allows preparing in high yields and selectivity a stable chiral hydrofuroin derivative which may serve as building block for new ligands, active ingredients or polymers, among other applications of chiral 1,2-diols.
A company of the coatings sector contacted ICIQ to develop innovative polymers based on monomers prepared thanks to this technology. The project did not prospere as a consequence of the adquisition of the coatings division of this company by another one.
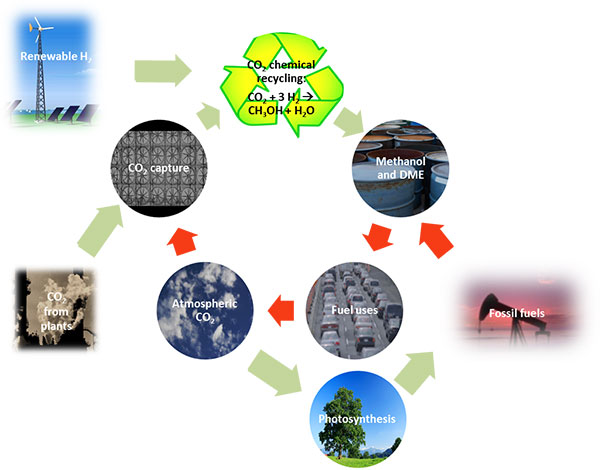
Process for the preparation of methanol and methanol-derived products from carbon oxides.
Chemical reduction of carbon dioxide to methanol and its derivatives (such as DME) is considered one of the key technologies to reduce both global warming and fossil fuels dependency. Unlike the currently used process for methanol synthesis, ICIQ’s process provides excellent conversions and selectivity to methanol in one pass through the reactor, thereby providing the highest time yield observed for the chemical reduction of CO2.
This technology has been the object of negotiations and scheduling of a joint development project associated to a progressive technology transfer scheme with a global petrochemical company. In spite of successful early negotiations, the company finally decided to retract.
SCIPIO: a comprehensive software interface for computational chemists
SCIPIO is a software that allows to handle, store and manipulate output files from computational chemistry experiments. SCIPIO is a general data extractor and manager that is here presented as a Computational Chemistry Results Repository, which is a sort of tailored electronic notebook allowing for substructure searches and for the generation of “ready to publish” reports.
Process for the preparation of cinchona alkaloid derivatives
Quinine and quinidine (natural products), can be transformed into eight structurally different compounds useful in organocatalysis and cascade processes of enolizable compounds. The synthesis allows for the conservation of the chiral centers. The obtained compounds, cinchona alkaloid derivatives, can be used as metal-free catalysts for the preparation of complex scaffolds in a limited number of steps within cascade reactions. Other applications include asymmetric Michael additions, fluorination of ketones, etc.
Some compounds of the invention prepared according to the optimized process are being commercialized by the company Strem Chemicals.
A compound comprising ruthenium nanoparticles supported on a solid support for the hydrogenation of aromatic compounds
A highly active and stable heterogeneous catalyst consisting in ruthenium nanoparticles stabilized with phosphine ligands embedded into a solid support has been developed. Hydrogenation of aromatics can be operated under mild conditions and under solvent free conditions, thereby rendering the process more sustainable and easy to implement. The catalyst can also be recycled at least 10 times without significant loss of activity, which makes it attractive for continuous flow applications.
Ratiometric assay for the quantification of hydrolytic enzymes
A nanoparticle containing two different populations of chromophores and funcionalized with a dye-labelled peptide sensitive to the action of a hydrolytic enzyme has been developed. In that way, the optical response of the system can directly be correlated, in a quantitative manner, to the activity of a specific enzyme found in the medium where the nanoparticle is placed, thereby allowing for enzyme quantification. This technology was applied to cystic fibrosis, through the analysis of the trypsin amount of faeces samples. It was shown that this system could allow for the determination of patient’s phenotype, thus avoiding genetic testing.
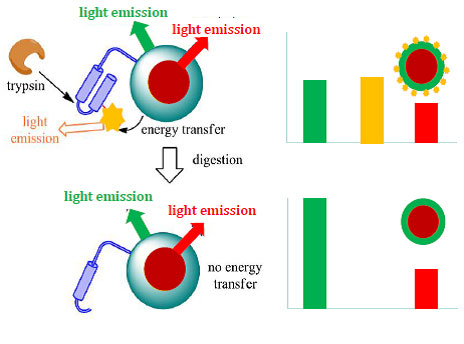
This technology will be further developed within a project of clinical validation of the diagnosis method funded by Fundació La Caixa.
Bis-salphen compounds and carbon-based composite materials comprising them.
A family of compounds able to form a network of rings interconnected by rods at the micro/nanoscopic scale through a self-assembly process has been developed. These compounds could successfully be incorporated into plastic materials in which the characteristic assembly is conserved. Within a polymer matrix containing carbon materials such as carbon nanotubes (composite material), the carbon particles aggregate around the self-assembled network, forming a network of dispersed and interconnected carbon materials, giving rise to e.g. lower percolation thresholds.
This technology was developed through a partnership with the German company Polymaterials AG. A TECNIOSPRING grant (ACC1Ó) was granted for the development of commercial applications of the technology within a collaboration between ICIQ and Polymaterials AG, with a clear focus on market-driven research and technology transfer (project is to start in 2014).
Composicions de pentafluoroetilació
A process for the direct cupration of pentafluoroethane has been developed. This exceedingly simple process employs only cheap reagents and is advantageously run at room temperature to produce CuC2F5 reagents that are useful in pentafluoroethylation reactions. Chemical compounds bearing a pentafluoroethyl group are widely used in the production of various pharmaceuticals and agrochemicals as well as specialty materials, polymers, composites, building blocks, and intermediates for various needs. Pentafluoroethane, C2F5H, is an ideal source of C2F5 because it is inexpensive, readily available in large industrial quantities and non‐toxic.
Polymer supported phosphoric acis and use thereof in the preparation of 3-indolylmethanamines
3-indolylmethanamines, and more particularly their chiral derivatives, constitute a relevant family of compounds for the crop protection and pharmaceutical industries. The invention provides a polymer-supported organocatalysts that is highly active and selective for the preparation of such compounds by Friedel-Crafts reactions. Being supported on a polystyrene resin, the catalyst is easily recyclable by filtration and can be used under continuous flow conditions, making it suitable for process intensification and the preparation of libraries of chiral compounds.
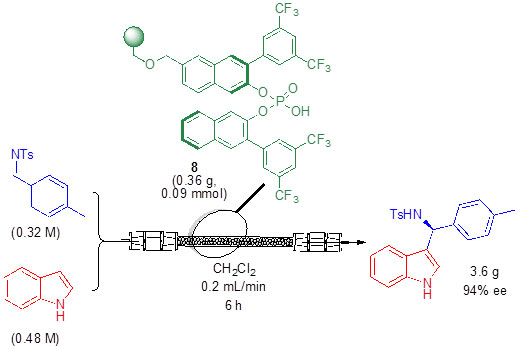
This technology will be further developed within a valorization project funded by Fundació La Caixa.